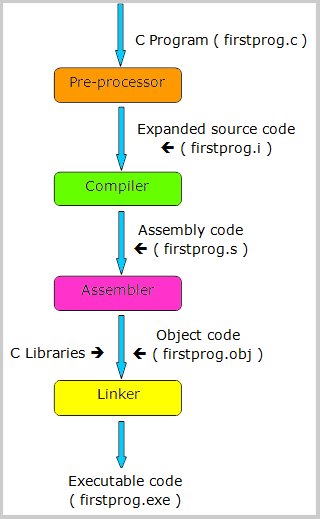
Compilation process in C language
The C compilation method converts the source code into the object code or machine code. The compiler checks the source code for syntactic or structural errors and produces the object code.
The method of compilation process can be divided into four stages, i.e., Pre-processing, Compiling, Assembling, and Linking.
- Pre-processor - The pre-processor takes the source code ".c" file as an input, and it extracts all the statements removing comments from the source code. If <stdio.h>, the directive is available in the source code, then the preprocessor interprets the directive and replace it with the content of the "stdio.h" file.
- Compiler - The source code expanded by the pre-processor is passed to the compiler. The source code is converted into assembly code by the compiler that means the C compiler transforms the pre-processed code into assembler readable code.
- Assembler - The converted assembly code is translated into object code with the help of an assembler. The name of the object file is same as the source file with extension of ".obj" in DOS or ".o" in UNIX operating system. If the source file is "firstprog.c", then it would be the object file "firstprog.obj".
- Linker - The linker combines the object code with required C library functions to make an executable program. This step typically involves adding in library files that are required and combines them into a single executable file, library file, or another "object" file.
Let us look at the steps of execution of C program "firstprog.c" :
ADVERTISEMENT